Keills, Chapel And Graveyard
Burial Ground (Medieval), Chapel (Medieval)
Site Name Keills, Chapel And Graveyard
Classification Burial Ground (Medieval), Chapel (Medieval)
Alternative Name(s) Cill Mo-charmaig; Kilmacharmick; Keillmore; Church Of Saint Cormac
Canmore ID 38654
Site Number NR68SE 2
NGR NR 69134 80538
Datum OSGB36 - NGR
Permalink http://canmore.org.uk/site/38654
First 100 images shown. See the Collections panel (below) for a link to all digital images.
- Council Argyll And Bute
- Parish North Knapdale
- Former Region Strathclyde
- Former District Argyll And Bute
- Former County Argyll
Desk Based Assessment (1964)
NR68SE 2 69134 80538
(NR 6913 8054) Chapel (NR) (In Ruins)
OS 6" map (1924)
Cill Mo-Charmaig, called Kilmacharmick by Blaeu, was at Keills. The saint referred to is St Cormac.
W J Watson 1926
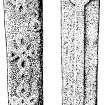
This roofless chapel dedicated to St Charmaig (J R Allen and J Anderson 1903) measures 43' x 20' externally, 36' x 16' internally. An arched doorway on the S has been blocked, but can be traced; there is a round-headed window in the E end. There are many fine cross-slabs in the chapel and graveyard. The positions of the more important are shown on W C Crawford's (1920) plan.
M Campbell and M Sandeman 1964
Information from OS.
Field Visit (14 May 1973)
The chapel as described, is currently being renovated by the DoE. The dedication could not be confirmed. All of the so-called cross slabs are in fact grave markers.
Visited by OS (DWR) 14 May 1973
Field Visit (20 January 1977)
As described in the previous information, except that renovation is complete and the chapel is now roofed.
Surveyed at 1/10,000.
Visited by OS (TRG) 20 January 1977.
Measured Survey (2 May 1985)
RCAHMS surveyed Keills Chapel on 2 May 1985 with plane-table and alidade producing a ground plan at a scale of 1:100 and window details. The plan was redrawn in ink and published at a scale of 1:250 (RCAHMS 1992, 84B) and the east windows details at a scale of 1:50 (RCAHMS 1992, 84E).
Field Visit (August 1989)
The medieval church of Knapdale parish is situated 300m SE of Keills Port (No. 271) on a hillside sloping SE to Loch na Cille, an inlet of the Sound of Jura. The church, which probably dates from the last quarter of the 12th century, looks SE across the island of Danna to Castle Sween (No.119) and SSW to Eilean Mor (No. 33), whose medieval chapel shared the same dedication to the Leinster saint Abban moccu Corbmaic. The building was re-roofed by SDD(Ancient Monuments) in 1978 to house the important collection of Early Christian and medieval carved stones(infra), and in 1979 the free-standing Keills Cross (number 1)was moved inside from its position on a higher terrace 50m to the NW.
The existing rectangular churchyard-wall is of 19th-century construction, and although there are remains of old tracks and pre-improvement buildings W and SW of the church, there is no visible evidence of an early enclosure. The church measures 10.9m from E to W by 4.8m within walls varying from 0.75m to 0.9m in thickness, which survive to full height including the gables. The masonry is of quartzite and other local rubble, including edge-set slabs and boulders, not squared but brought to level courses with schist pinnings, although the N wall is less regular than the others.
A broken millstone at least 0.7m in original diameter and with an 80mm aperture is built into the outer face of the S wall at a height of 2m, and another re-used fragment with a curved chamfered edge and bearing a perforated boss is built into the inner face of the same wall at a similar level. Rubble is used for most of the quoins, those at the NW angle being of 'side-alternate' slabs, but sandstone is used in the upper part of the NE angle, above well-squared rubble blocks, and is mixed with rubble in the upper part of the SE angle. The ground-level falls about lm from W to E, and some parts of the S wall are built directly on outcropping rock, while the E wall is founded on a level plinth. There are considerable remains of harling in the SE angle, and other evidence of it on both internal and external wall-faces. The modern roof is slated, with skylights on the S slope.
The church is entered by a rebuilt N door and lit by a small window, which largely retains its original form, and by opposed windows near the E ends of the side walls and another in the S wall of the nave, all of which, like the doorway, have been much altered and are now flat-lintelled. The E window has a round-arched splayed embrasure with rubble jambs and sandstone voussoirs, and the inner edge of the stepped sill is chamfered, probably on the alignment of an original splayed sill. The external sandstone rybats have been cut back to enlarge the daylight-opening, but the schist sill preserves evidence of a 40mm external rebate, indicating an original opening 0.73m high by 0.2m wide, and an outerincised 70mm margin which is not visible on the weathered sandstone above. The external opening of the SE window has been destroyed, but the schist sill indicates a 115mm daylight opening,with an external 50mm chamfer; there is some sandstone in the splayed inner rybats, but the E ingo is not aligned with the outer sill and may have been rebuilt. This wascertainly the case with the splayed jambs of the NE window, where the schist sill preserves the position of an earlier daylight-opening a little to the W of the existing one. The second window in the S wall appears to show a splayed embrasure which has subsequently been enlarged to the w, but all of the masonry has been altered and its date is uncertain. The N doorway, which has rubble jambs and a roughly bevelled external lintel, was rebuilt between about 1870and 1890 (en.1). There are two identical aumbries, each 0.25mhigh, at the ends of the inner face of the E wall, with a smaller one below the N jamb of that at the S end, and an excavation in 1977 exposed an altar-base, 1.3m by 0.85m, below the E window. Numerous burials were found in the area excavated, three of them being on a different alignment and possibly pre-dating the church, but the burials in the three tomb chests covered by medieval slabs (numbers 20-22) were of19th-century date (en.2). The steps leading down from the W end, installed by SDD in 1978, evidently perpetuate a medieval change in floor-levels, but there is no evidence where this took place originally.
The Keills Cross (infra, number I), dating probably from the late 8th or early 9th century, indicates that this was an important ecclesiastical site at that period, but its nature is uncertain, and there is no evidence of monastic occupation like that on Eilean Mar (No. 33). The name CiIl Mhic O’Charmaig, recorded in a variety of forms between the 13th and early 19th centuries, appears to incorporate the name of Abban moccu Corbmaic, the founder of two monasteries in Leinster, who was probably active in the 6th and early 7th centu ries (en.3). The existing building appears to date from the second half of the 12th century and, like contemporary churches in Kintyre, is probably associated with the beginnings of a parochial system in Argyll. Until the subdivision of Knapdale parish in 1734 this was the principal church for the whole of Knapdale except for the Kilberry area (see No. 48), although there were chapels at Kilmichael of lnverlussa (No. 70) and Kilmory Knap (No. 76). The patronage of both of these was granted to Kilwinning Abbey by Waiter Stewart, Earl of Menteith, before 1294, along with the parish church of 'Kilmachermat in Cnapedale' and the three pennylands of 'Riventos' belonging to it, while bishop Andrew (1300-c.1327) added the parsonage revenues, although reserving a portion for a perpetual vicar. The other early 13th-century chapels at Cove (No. 94) and Eilean Mor (No. 33) were not affected by these grants and in the late middle ages they were apparently in the patronage of the Lords of the Isles. Maurice, parson of 'Chillmacdachormes', is recorded as a witness before 1222, and a royal presentationto the vicarage was made in 1551 (en.4).
The church at Keills remained in use for most of the 17th century, and in 1628 a meeting of the kirk session was held there during which a violent brawl occurred in the churchyard (en.5). During the 1640s, however, there were proposals to separate Keills from Kilmichael of Inverlussa, and although these were abortive, the latter remained the normal place of residence of the minister. In 1649 it was complained that the interior of the church at Keills was still being used for burials, contrary to an act of the general assembly. A further violent altercation took place in 1677, when Archibald Campbell of Danna 'for his owne accomodatione ... caused build and erect ane dask (desk) and seatt in the said kirk ('Kilvicocharmick')’, which was demolished by a neighbour 'immediatlie before divine service'. The church probably went out of use soon after this, and in the following century a preaching house at Tayvallich was subordinate to the parish church of North Knapdale at Kilmichael of Inverlussa (en.6). The roofless building was repaired in the last quarter of the 19th century, and came into state guardianship in 1972.
RCAHMS 1992, visited August 1989
[see RCAHSM 1992, No. 45, for a full description of funerary monuments, crosses and other carved stones]
Project (August 1994)
It was proposed that a new roll-on-roll-off ferry route to be opened linking Jura directly to the mainland. The suggested route is between Keills on the Tayvallich peninsula and Lagg on Jura.
To fulfill the archaeological requirements of an environmental impact assessment prior to the granting of planning permission, GUARD were contracted to undertake a program of documentary research and field survey focussed on the two slipway locations and including the road between Keills and Tayvallich which may require upgrading. The work was commissioned by the Centre for Environmental Management Studies at the University of Strathclyde and was completed in August 1994.
GUARD 1994
Reference (2001)
Medieval church of 'Kilvicocharmick', probably dedicated, like Eilean Mor (No.33), to the Leinster saint Abban moccu Corbmaic. Re-roofed in 1978 to house large collection of early and late medieval stones.
(1) THE KEILLS CROSS (see NR68SE 1).
(2) Slab NR68SE 2.01
(3) Slab NR68SE 2.02
(4) Slab NR68SE 2.03
(5) Slab NR68SE 2.04
(6) Slab NR68SE 2.05
(42) Fragmentary cross-head and -shaft NR68SE 2.06
I Fisher 2001.
Note
NMRS REFERENCE
Keills Chapel.
NMRS Preliminary Excavation Report 1977 - photocopy of typescript.