Ardoch
Temporary Camp (Roman)
Site Name Ardoch
Classification Temporary Camp (Roman)
Alternative Name(s) Black Hill; Braco; Ardoch Bridge; Ardoch, Roman Military Complex
Canmore ID 25391
Site Number NN81SW 18
NGR NN 8420 1080
NGR Description Centred NN 8420 1080
Datum OSGB36 - NGR
Permalink http://canmore.org.uk/site/25391
- Council Perth And Kinross
- Parish Ardoch
- Former Region Tayside
- Former District Perth And Kinross
- Former County Perthshire
NN81SW 18 centred 8420 1080
ROMAN CAMPS
(remains of) [R]
[centred NN 8423 1069]
OS 1:10,000 map, [1982].
For further information see NN80NW 10.
For other elements of Ardoch, Roman Military Complex , see:
NN80NW 10 NN 8390 0990 Fort
NN80NW 32 NN 8425 0999 Fort (Formerly entered as Temporary Camp)
NN81SW 7 NN 8452 1075 Watch Tower (Scheduled as Signal Station)
NN81SW 15 NN 8390 1090 Temporary Camp ('63 acre')
NN81SW 16 NN 8370 1060 Temporary Camp ('30 acre')
NN81SW 17 NN 8380 1050 Temporary Camp ('13 acre': within NN81SW 16)
NN81SW 19 NN 8404 1022 Temporary Camp (Scheduled as Annexe to Fort NN80NW 10)
NN81SW 40 Camelon - Ardoch - Strageath - Cargilll Roman road (RR 9a) [Scheduled length from NN 8425 1034 to NN 8486 1127].
A probably Flavian 120 acre camp.
J K St Joseph 1970.
Scheduled (with NN81SW 15) as 'Ardoch, Black Hill, Roman camps... the remains of parts of two overlapping Roman temporary camps, the ramparts of which survive in parts as upstanding earthworks'.
Information from Historic Scotland, scheduling document dated 7 June 2004.
Scheduled as 'The largest camp' [covering] an area of around 130 acres' within 'Ardoch, Roman military complex 900m NNE of Ardoch Bridge...'
Information from Historic Scotland, scheduling document dated 26 March 2008.
Excavation (September 1977)
Over two weekends in September 1977 a small excavation was conducted with the aid of technical staff and students of the Department of Archaeology, Glasgow university at the northern intersection of the two largest marching camps at Ardoch in order to establish their chronological relationship.
Information from William Hanson.
Excavation (August 1997 - August 1997)
NN 8452 1075 Excavation on the site at Blackhill Wood was commissioned in response to substantial damage being caused to the monument, principally by rabbit burrowing and tree roots. Surveys were undertaken to assess the level to which both of these agents had affected the remaining evidence. It was also hoped to supplement the information gained from Professor J K S St Joseph's trenches at the site, from 1974.
The site was defined by two concentric, sub-rectangular, V-shaped ditches with an external diameter of 25.2-26.3m. Associated with these were outer and medial banks of upcast material and an inner turf work. The inner ditch surrounded an area of 11.2-12.3m, which contained the inner turf work and the remains of a 4-post tower structure.
The ditches differed in size with the outer being the slighter (2.5-3.4m wide by 0.3-0.5m deep), while the inner measured 2-2.5m wide and 0.5-0.8m deep. Upon excavation it was confirmed that the outer ditch did not continue around the southern side of the site where the ground slopes off to the S. An oven, with a stone-paved base, was located cut into this slope. From the fill sequence it is difficult to say whether this was contemporary with the signal station or the temporary camp. The entrance to the signal station faced towards the Roman road which lay 30m away to the W.
Three post-holes were located with a fourth one assumed to lie under a large oak tree. They were fairly similar in size being over 1m in diameter, and 0.95-1.01m deep. The NE post-hole exhibited three phases of use. From this evidence the dimensions for the tower structure would appear to have been around 3.5m (SE-NW) by 3.7m (NE-SW).
Within the area bounded by the post-holes, ie the interior of the tower, paving was located on top of a levelled surface; repair to this paving was also evident.
A small amount of excavation was carried out on the defences of the temporary camp, to confirm St Joseph's observations about the relationship between the sites. The temporary camp was stratigraphically later than the signal station. The camp defences were a standard V-shaped ditch with an upcast inner rampart.
As with all Gask sites finds were rare. They include an unstratified sherd of coarse ware, a square-headed nail from within the area of the tower, and a stone incised with linear grooves from the sharpening of iron blades from the inner ditch of the signal station. There were no finds from the temporary camp.
B Glendinning and A Dunwell 1997.
Publication Account (17 December 2011)
The Flavian and Antonine fort at Ardoch has long been known and identified with the Roman army (see Christison 1898). On the plain to the north of the fort lie five camps of varying sizes, first apparently identified as ‘several larger squares’ by Sibbald (1707, 37), with two camps recorded and planned by Roy in 1755 (1793, Pl. X). Parts of these two can still be traced on the ground today. Pennant depicted these two stretches along with a third earthwork, which may well represent the east side of Ardoch III (1776, 103, Pl. X).
A further possible camp is recorded at Nether Braco across the River Knaik to the west, and another immediately to the east of the fort (St Joseph 1976, 14) was re-interpreted as another fort following excavations in 1977 (RCAHMS St Joseph Collection: Notebook 7).
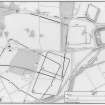
Camp I (NN 81 SW 18), the largest in the complex, measures 874m by about 600m, and enclosed 52 ha (129 acres) of gently undulating ground. Stretches of the south-east and south-west sides, including a titulus, survive as earthworks. Most of the remaining perimeter ditch, and the northern titulus, have been recorded as cropmarks. It is assumed from the position of the tituli that the camp probably had six gates. The camp intersects several other camps on the complex, and a watchtower in Blackhill Wood on its south-east side. Here, excavations have recorded that the perimeter of the camp overlies the presumed Flavian tower (St Joseph 1977a, 135, fig. 8; Glendinning and Dunwell 2000). The ditch at this point was V-shaped and measured about 3.6m wide and 1.25m deep. Excavations on the west side where the camp overlaps camps II, III and IV, recorded that the ditch of the camp was wide (2.7-3m) but very shallow, cut only some 0.3m into the subsoil then left unfinished. It stopped short of the ditch of camp II, suggesting that it was later (St Joseph 1970a, 170-1), and also stopped short of Camp II at the north intersection of the two (Hanson 1978a, 148). The upstanding segment of ditch on the north-west side is significantly deeper than that recorded by St Joseph’s excavations, demonstrating the differential survival rates and, quite possibly, the differing depths constructed by troops in antiquity. The excavations on the south-east side recorded that the ditch appeared to have silted up naturally (Glendinning and Dunwell 2000, 277). A titulus was also excavated on this side, the ditch of which was recorded as 2.9m wide and 1.55m deep (Glendinning et al 2000, 262). The intersection between camps I and V has also been excavated, with camp I recorded as the later of the two (St Joseph 1976, 19).
The finds from the watchtower excavation were dated to the 1st and 2nd centuries, but were unstratified. An oven was located just inside the perimeter between the ditches of the watchtower; this probably relates to the occupation of the camp rather than the tower (Glendinning and Dunwell 2000, 287).
Camp II (NN 81 SW 15) lies to the north-west of camp I, intersecting its north-western side. A short stretch of its south-eastern side survives as an upstanding earthwork but the remainder of the camp has been recorded as cropmarks. It measured about 635m from north-east to south-west by about 440m transversely and enclosed almost 27 ha (66 acres). Tituli are visible in the centre of the north-east and south-west sides with a further two on its north-weat side suggesting that it had six entrances in total. Excavations where the camp overlaps camps I, III and IV recorded that the ditch was up to 2.7m wide and 1.2m deep. It had been deliberately in-filled where it lay within Camp I, particularly on the line of the rampart of that camp (St Joseph 1970a, 167-71).
The camp has an annexe on its north-east side, measuring 118m by 85m and enclosing an additional 1 ha (circa 2.5 acres).
St Joseph observed that the gap in the camp earthwork on the south-east side is exactly between the presumed gates of camp I; this suggests that camp I is the later of the two, the rampart of camp II being flattened for the street lines of this later camp (1976, 17). He also comments that hardly any silt had accumulated in the ditch at this point and that therefore there was little time difference between the construction of the two camps (1976, 19). It is unclear when this section was excavated, although it may have been in 1970 (RCAHMS St Joseph Collection: Notebook 5).
Camp III (NN 81 SW 17) was re-discovered from the air in 1948 (St Joseph 1951, 62; 1955, 87), but was partially recorded in 1772 by Pennant (1776, 103, Pl. X). It overlaps the southern corner of camp II and the south-west side of camp I and is now wholly known as a rectangular cropmark measuring 263m from north-east to south-west by 205m transversely, enclosing 5.3 ha (just over 13 acres). Excavations by St Joseph in 1969 recorded that the ditch was some 2.3m wide and nearly 1m deep on its north-west side. The ditch had been deliberately filled (and contained tiny fragments of coarse ware and mortaria), which he interpreted as taking place due to the enlargement of the camp into camp IV. A trench under the presumed line of camp II suggested that there were two phases of in-filling, one for the construction of camp IV and the other for camp II (St Joseph 1970a, 167-9). However, given the small-scale nature of the trenches, it is perhaps rather ambitious to be so confident on the fill of the ditch. He also commented that this camp must be early in the sequence at Ardoch because it occupied the best location close to the fort (1969, 114). No entrances are known but there is a possible gap close to the centre of the north-west side.
Camp IV (NN 81 SW 16) was also discovered from the air in 1948 by St Joseph (1951, 62; 1955, 87), and was seen by him as an extension of camp III. On the assumption that it shares three of the sides of camp II, it measures around 450m from north-west to south-east by 266m transversely, enclosing about 11.8 ha (29 acres). No gates are known.
The enlargement of camp III to become camp IV is not the only possibility for deliberate re-filling of the ditches, because St Joseph’s trenches were also within camp I. Furthermore, the dangers inherent in attributing periods of time to ditch silting and back filling have been exemplified at Ythan Wells (Hanson 1978, 145). It is also possible that camp IV was later reduced to become camp III.
Camp V (NN 81 SW 19) was discovered in the 1970s by St Joseph following a re-examination of Roy’s field boundaries (1976, 19; 1977a, 137) and lies within the annexe (so-called ‘Procestrium’, a term coined by Roy), north of the fort. It survives as a low earthwork measuring 220m from north-south by 197m transversely, enclosing 4.3 ha (10.7 acres). St Joseph placed numerous trenches through this camp between 1975-8 to determine its full extent. The rampart measures up to 2.7m wide and 0.3m high, with the excavated ditch up to 1.6m wide and 1.2m deep. Elsewhere, the ditch is visible as a hollow, some 2.4m wide. It appears to have been deliberately filled in, and St Joseph suggested that the camp must be earlier than the annexe because the earthworks of the latter block all visibility (1976, 19; 1977a, 138). It is also overlain by camp I (St Joseph 1976, 19).
Camp V possesses an annexe on its south side, which measures up to 140m by some 42m, enclosing an additional 0.6 ha (1.45 acres). Excavations in 1977 on this annexe revealed that its ditch was up to 1m deep and 1.5m wide (RCAHMS St Joseph Collection: Notebook 7).
The five camps have therefore been subject to various excavations over the years, principally to establish the sequence between them, because members of St Joseph's '30-acre', '63-acre' and '130-acre' series are represented. These have led to statements on chronologies but some are suppositions and not all are fully sustained by the evidence.
From the earthworks, Roy concluded that camp II was later than camp I (1793, 62-3) but Hanson examined an original drawing of Roy’s plan which depicted camp I cutting camp II (Hanson 1978, 148). This chronology was confirmed by two excavations at the intersections of camps I and II, where camp I stops short of camp II in two locations (St Joseph 1970a, 170-1; Hanson 1978, 148). Camp I also overlaps the Gask Ridge watch tower of Blackhill Wood to the east. To the south it overlaps camp V and the annexe north of the fort. It is clearly later than the watch tower and also later than camp V (St Joseph 1977a, 138). There is some debate regarding its relationship with the annexe of the fort. It was widely believed that the earthworks of the annexe override the south-east corner of camp I (Roy 1793, 63; Crawford 1949, 33; Breeze 1973, 126), although St Joseph disputed this, stating that the camp was the later of the two (1977a, 135). At the west intersection of the two, the annexe appears to be later, but this may have been re-cut as a field boundary (Hanson 1978, 146). However, at the eastern intersection the camp does appear to overlie the annexe.
Thus the main chronological evidence for the camps appears to be that camps II and V are earlier than camp I, which possibly represents one of the latest phases of occupation of the site. Camp I was constructed after the watch tower, and is therefore likely to be post-Flavian in date. It also appears to be later than the ‘Procestrium’, which is probably an annexe for one or more phases of the fort - at the latest Antonine II. That camps I and II are later in the sequence could explain the better survival of their earthworks into the 18th century, but part of camp III also appears to have been recorded (Pennant 1776, 103, Pl. X). Camps III and IV probably pre-date camps I and II, but the sequence between these two is not yet defined.
R H Jones 2011
Watching Brief (18 July 2013)
An archaeological watching brief was undertaken during the replacement of a pole on an overhead power line near the village of Braco, Perthshire. The original intention was to monitor the replacement of two poles but only one was changed during this exercise. The refurbishment was carried out by Scottish & Southern Energy (SSE) whose representative, Denise Harbut, commissioned the watching brief, undertaken by John Lewis of Scotia Archaeology on 18 July 2013.
Pole 1 was located at NN 84306 10602, in a gently undulating hay field which, unlike some neighbouring fields, had not been cropped at the time of the watching brief. The trench for the new pole was excavated to the immediate north-west of the existing one. It measured 1.5m north-west/south-east by 0.7m wide and 1.5m deep. It cut through 0.2m of red-brown ploughsoil, containing much gravel, and underlying glacial till of red-brown sand, gravel, pebbles and boulders.
No structures, features or deposits of archaeological significance were uncovered within this trench and no artefacts were retrieved from it.