Yester Castle And Goblin Ha'
Motte And Bailey (Medieval), Tower House (Medieval)
Site Name Yester Castle And Goblin Ha'
Classification Motte And Bailey (Medieval), Tower House (Medieval)
Alternative Name(s) Hobgoblin Ha'; Goblin Hall
Canmore ID 56062
Site Number NT56NE 1
NGR NT 5563 6668
Datum OSGB36 - NGR
Permalink http://canmore.org.uk/site/56062
- Council East Lothian
- Parish Yester
- Former Region Lothian
- Former District East Lothian
- Former County East Lothian
(NT 5563 6668) Yester Castle (NR) (Remains of)
Hobgoblin Ha' (NR) Subterranean Cavern (NAT)
OS 6" map (1957).
Not to be confused with Yester House (NT 54348 67161), for which see NT56NW 17.00.
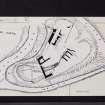
Yester Castle is built on a slightly crescentic peninsula, with precipitous sides leading to Hopes Water on the E, and a tributary on the W. A ditch, 100ft wide from crest to crest and 20ft deep, at the S end, isolates the site from the mainland, while a second ditch, 30ft wide and 15ft deep, is cut across the N end.
The level portion of the site has been bounded by walls 6ft to 8ft thick, against which internal structures have been raised. These have mostly been levelled, though portions still stand on the N and E to a height of 40ft. The most prominent portion of the curtain wall still standing is the N side, complete for its length of 70ft, and 20 and 30ft respectively of the walls returning along the flanks. In the NE corner are the foundations of secondary buildings.
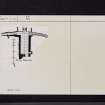
Within the enceinte, against and embodying the E curtain, is a range of building which has been three storeys in height and dates from the end of the 15th century. On the W of the enceinte are the remains of another range of buildings now only a few feet above ground, and from the most northerly of these, a stair leads down to the "Goblin Ha'", an oblong chamber 37ft by 13ft 2ins, built of ashlar.
At the S end, towards the W corner, the conformation of the debris would suggest that the curtains were originally strengthened by circular towers, but this, and other obscure points, can only be proved by excavation.
The "Goblin Ha'" may date from the 13th century and the western range was probably built towards the end of the 14th century, while the masonry of the enceinte walls would appear to be of 15th century date.
E of the site, a fragment of masonry, probably the central pier of a bridge, 12ft broad and 8ft thick, stands in the centre of the Hopes Water. The smaller stream is crossed by a bridge with masonry of considerable age, but by no means as old as the fragment, which might well be 15th century work.
D MacGibbon and T Ross 1887; RCAHMS 1924, visited 1915.
The 'Goblin Ha'' is the undercroft of a 13th century tower, reduced in height to make way for a later reconstruction of the castle lay-out. Originally it was partially dug into the mound of a motte. After the reduction of the upper works, the undercroft was covered over.
W D Simpson 1952; S Cruden 1960.
Yester Castle and Hobgoblin Ha' are generally as described; the interior of the castle is now heavily overgrown. The remains of the bridge pier are at NT 5566 6670.
Visited by OS (BS), 21 August 1975.
Field Visit (14 April 1915)
251. Yester Castle.
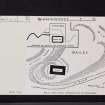
Yester Castle (fig. 183) is built on a promontory formed by the confluence of the Hopes Water with a tributary running northwards from Castlemains farm about 2 miles south-east of Gifford.
The peninsula lies north and south and is slightly crescentic in shape, with precipitous sides bounded by the waters 50 to 70 feet below. At the southern end a ditch, measuring 100 feet wide from crest to crest and 20 feet deep, has been excavated, isolating the main site from the mainland. The site is level with the landward for a length of 200 feet, beyond which it falls rapidly on the north to the water level; in this direction a second ditch, 30 feet wide and 15 feet deep, is cut across the head of the peninsula 230 feet north of the first and at a considerably lower level. The geological formation of the site is readily seen in the banks of the water courses, where it is found to be composed largely of a soft reddish sandstone rock with a covering of loam, easily excavated.
East of the position, where the Hopes Water takes a westward loop, a fragment of dressed masonry 12 feet broad and 8 feet thick is seen in mid stream, suggesting from its position that it formed the central pier of a bridge. To the south-west the smaller stream is crossed by a bridge with masonry of considerable age but by no means as old as the fragment on the east, which might well be 15th century work.
The level portion of the site measures about 200 feet from north to south and has a greatest width of 120 feet from east to west (fig. 14). It has been girt by great walls of enceinte 6 to 8 feet thick, against which internal structures have been reared. These for the most part are levelled to the ground save on the north and east, where portions still stand to a height of 40 feet. In other directions the walls have fallen, and their debris litters the flanks of the enceinte and the interior, rendering the arrangement difficult to elicit. At the southern end, towards the western corner, the conformation of the debris would suggest that the curtains were here strengthened by circular towers; but these and many other obscure points can be ascertained only by extensive excavations.
The most prominent portions of the curtain still standing are the northern side, which is complete for its length of 70 feet, and 20 and 30 feet respectively of the walls returning along the flanks. The masonry is built of reddish freestone ashlar set in large courses and is covered with a dense growth of ivy. At the base of these walls a heavy offset course with a weathered top returns exteriorly. In the northern wall, at the level of the enceinte, an arched doorway, which has been closed by double doors, gives access to the northern portion of the site, beneath which is the subterranean chamber known as the “ Goblin Ha’ ” . On the interior of this wall can be seen the beam-holes for two floors above the level of the enceinte, and on the west wall, on the floor above this level, is a slightly projecting basin with an ogival head and an external outlet with a stone spout. In the north-east corner are the foundations of secondary buildings, which have been covered with a penthouse roof, the sloping raggle for which can be seen on the interior of the north wall. These and the other buildings have been roofed with stone slates, several fragments of which can be seen amongst the debris.
A ruinous stone staircase leads down beneath the north wall to what is now the most interesting and the only complete chamber of the castle, the "Goblin Ha'" (fig. 80). It is an oblong chamber 37 feet long and 13 feet 2 inches broad, set not rectangularly to the northern wall of enceinte but inclined to the north-east. It is built of ashlar and is roofed with a pointed stone vault with massive close set ribs; these are mortised at springing level to receive the joists of a mezzanine floor; both floors are entered from pointed arched doorways on the south but are otherwise unlighted. Adjoining the lower doorway at the south-east angle is a cupboard with an arched head, checked for a door and penetrating 6 feet within the wall. In the north wall is a fireplace opening of early type. Some 6 feet above floor level are two massive corbels 5 feet apart, on the outer sides of which are lesser corbels; immediately over each main corbel is a beam-hole penetrating some 6 feet within the wall, and above this level the breast of the fireplace is splayed back, as it ascends upwards, to a square flue emerging in that portion of the site north of the main wall of enceinte. Bearers would be inserted in the beam-holes and would have a further support on the large corbels; these joists would support a sloping hood. The lesser corbels probably were intended as rests for lamps or vessels.
In the northern end of each of the lateral walls is a high pointed arched doorway with slots in the ingoings for the massive bars which secured the doors; beyond these doors may be seen the start of a passage covered with a pointed vault. These doorways have probably been intended as sally ports emerging midway down the steep slope on the flanks of the site. At a subsequent period these have been altered; that on the west is contracted, and a lower vaulted passage emerges well down the slope; the eastern doorway has been partially blocked up, and within it is formed the entrance to a straggling staircase which descends steeply for 20 feet, where it terminates under the north-eastern angle of the curtain against the solid rock. The staircase is narrow, merely sufficient for the passage of people in single file; the sides are lined with masonry inferior to that of the super-structure, and the roof is formed of a semicircular vault. For what purpose this elaborate passage was constructed is obscure*; still more so is the reason why the project was abandoned, unless the builders feared that further tunnelling would threaten the stability of the angle of the curtain.
On the higher level of the enceinte, the portion of the site above the “ Goblin Ha’ “ and beyond the curtain through which it is entered, has been apparently enclosed by a wall.
Within the enceinte, against and embodying the east curtain, is a range of building which has been at least three storeys in height and dates from the end of the 15th century. The lowest storey is ceiled with a semicircular barrel vault and contains a fireplace in the west wall and a slit-window in the east with a stepped sole. Above this vault only the east wall remains. The first floor has been ceiled in wood. It contains the remnants of a large fireplace, in the back of which are the sill and jamb of a window, not an uncommon occurrence in medieval work; adjoining the fireplace and to the south is an ogival-headed ambry. The floor above has been ceiled by a lofty stone barrel vault probably pointed in form. The only feature now remaining is the jamb of a lofty window, evidently intended to have a pointed arched head. On the arris of the jamb is wrought a shaft with an edge fillet and quirked flanking hollows. The shaft terminates in a belled base, dying out on a corbel. Within the jamb is a cupboard with a pointed arched head, entirely framed within bead-and-hollow mouldings returning around the foot and not, as is usual, received on a sloping sill. The opening is 1 ½ feet broad and 3 feet high; above the apex is a shield uncarved. The cupboard also has a pointed arched roof and is 4 ¼ feet deep and 3 ¼ feet broad.
On the west of the enceinte are the remains of another range of buildings now only a few
feet above ground, and from the most northerly of these the stair leading down to the “ Goblin Ha’ “ is entered. South of this may be traced an apartment, which has been lit by a two-light Gothic window on the east, the roll-and-hollow moulded jambs and the mullion seat of which remain in situ. A second and smaller window can be traced, which lighted this apartment from the south and opened apparently into a trance between these buildings and others farther south still more fragmentary.
The remains of the main entrance and others of the more important features which usually supply fairly conclusive evidence of date, are either buried or missing. The lower hall or “ Goblin Ha’ ” may date from the 13th century, and the western range was probably built towards the close of the 14th century. The masonry of the walls of enceinte is not unlike that found in early 15th century work, while the ogival-headed basin in the west wall and the detail of the eastern range is clearly 15th century work-and late rather than early.
Much could be done to preserve the ruins, which appear to have received no attention since falling into a state of disrepair. In particular the vegetation on the walls and vaulting should be removed, and the tops of the walls weather-proofed.
HISTORICAL NOTE.
Yester belonged of old to the family of Gifford (1) from whom, in the 14th century the lands passed to the Hays (2). In 1267 died ‘Hugo Giffard de Zester, whose castle or at least the cave and donjon (tower),as old stories tell, had been constructed by magic (arte dæmonica): for there is a marvellous subterranean cavern, wonderfully constructed and carried under a great extent of ground, which is popularly called Bohall’ (3). The castle was occupied by a constable for Edward II in 1311 (4).
The Lord of Yester's house’ figured in the operations by the English connected with the occupation of Haddington in the 16th century (5). On February 24, 1548, Lord Grey of Wilton got possession of it and committed its guarding to Sir George Douglas with fifty men. By the end of April, however, Lord Grey reports it as kept by Spaniards and holding out against the English fort at Haddington, so that it must have been recaptured by the Scoto-French forces. Again it fell into English hands, as on June 20 there was a request to Somerset for ‘one of the Frenchmen taken in Yester castle’ (6).
The place was abandoned as a residence at some date after the Reformation (7) but the present residence, Yester House, is of the period 1740-6 (8). The Hays of Yester quartered the arms of their predecessors the Giffords-gules, three bars ermine.
RCAHMS 1924, visited 14 April 1915.
(1) Cf. Introd. p. xxiii; (2) Cf. Introd. p. xxiii; (3) Scotich Lib. x., cap. 21; (4) Cal. Docts. iii., No. 218; (5) Cf. Introd. p. xxix; (6) Cal. Scott. Papers, i., Nos. 174, 228, 256; (7) Stat. Acct. i., p. 342; (8) Trans. Ed. Arch. Assoc. ii., p. 30.
* Sousterrains formed in the natural rock were a feature of Chateau-Gaillard, the castle raised by Richard I on the bank of the Seine; at Coucy may be seen in the court the mouths of vaulted galleries leading underground, which have never been cleared; and underground caves and passages are features of these fortified structures.
Desk Based Assessment (4 April 2022 - 14 April 2022)
A desk-based assessment has been carried out that has established that there are surviving remains ranging from national heritage value (high sensitivity) to local heritage value (low sensitivity) within the Forest Plan Site. These include the scheduled medieval ruins of Yester Castle; extensive areas of rig and furrow cultivation dating from the medieval to post-medieval period; enclosures and tracks relating to the layout of the Inventory Garden and Designed Landscape of Yester Estate; and various field banks and quarries probably dating to the development of the medieval estate and later uses in the 18th and 19th century. Furthermore, several designated heritage assets are situated in immediate proximity to the Forest Plan Site. Twelve of these remains would be directly affected to a greater or lesser degree by the Forest Plan and mitigation measures have been recommended to offset the predicted effects. The findings of the study indicate that there is a moderate potential for previously unrecorded archaeological remains to survive within the Forest Plan Site.
Information from OASIS Id: cfaarcha1-436583 (G Mudie) 2022
Field Visit (4 April 2022 - 14 April 2022)
A desk-based assessment has been carried out that has established that there are surviving remains ranging from national heritage value (high sensitivity) to local heritage value (low sensitivity) within the Forest Plan Site. These include the scheduled medieval ruins of Yester Castle; extensive areas of rig and furrow cultivation dating from the medieval to post-medieval period; enclosures and tracks relating to the layout of the Inventory Garden and Designed Landscape of Yester Estate; and various field banks and quarries probably dating to the development of the medieval estate and later uses in the 18th and 19th century. Furthermore, several designated heritage assets are situated in immediate proximity to the Forest Plan Site. Twelve of these remains would be directly affected to a greater or lesser degree by the Forest Plan and mitigation measures have been recommended to offset the predicted effects. The findings of the study indicate that there is a moderate potential for previously unrecorded archaeological remains to survive within the Forest Plan Site.
Information from OASIS Id: cfaarcha1-436583 (G Mudie) 2022