Field Visit
Date 2 August 2013
Event ID 980780
Category Recording
Type Field Visit
Permalink http://canmore.org.uk/event/980780
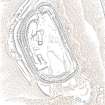
This fort crowns the summit of Denoon Law, a steep-sided volcanic plug on the NW side of Denoon Glen, a narrow valley at the N end of the Sidlaw Hills. The fort is roughly D-shaped on plan with the chord of the D formed by a long straight rampart that stands above the precipitous SE flank of the hill. It measures 105m from NE to SW by 55m transversely within a rampart that measures up to 17m in thickness and over 5m in external height but is clearly of more than one phase. Where the differentiation is clear, the latest phase of rampart measures about 6m in thickness and overlies the remains of a much thicker earlier rampart. Intermittently visible at the SW end of the fort is an outer face to the later rampart, comprising drystone walling that has, in places, been displaced downslope by the weight of core material behind. This outer face comprises no more than four or five courses of thin sandstone slabs and, although what is currently visible will only be the top of the surviving wall-face, a wall constructed of such material cannot have stood to any great height and what we see today is likely to be the remains of some form of comparatively low revetment. In both the earlier and later ramparts there is very little evidence of stone within the core and it appears that the material (boulder clay) for both has largely been derived from several large quarries within the interior of the fort. At the SW corner of the fort most of the rampart has been removed, leaving only the lower part of the outer talus. The fort, or at least its latest phase, had two entrances, one on the NE and another on the NW, both of which are crossed by the remains of a narrow, later, wall that runs around the entire circuit of the fort and may be associated with at least some of the buildings within the interior.
Outwith the main rampart there is a series of three outer ramparts, again with very little evidence for the use of stone in their construction, which run from the edge of the very steep slope at the NE end of the fort, around the N side to the entrance on the NW. All three lines of defence have been reduced to little more than terraces, though there is no evidence for them ever having been cultivated. At the entrance on the NW, the terminals of these ramparts (on both sides of the entrance) are obscured below outwash deposits from the slope above. To the SW of the entrance it is not at all clear what the relationship is between the defences of the fort and the enclosure that occupies the rocky and extremely uneven SW flank of the hill. This enclosure, which has an entrance on the W, could be some form of annexe or it could represent the SW end of an enclosure that once took in both this area and the rest of the summit.
Within the interior of the fort there are the remains of at least nine rectangular buildings, two of them large and open-ended and each overlain by a smaller, later structure. The freestanding buildings are represented by the footings of walls with inner and outer stone faces; close to the entrance on the NE, however, there are two buildings represented by simple rectangular platforms cut into the rear scarp of one of the prehistoric quarries in one case and the hollow of the entrance passage in another. On the N flank of the hill, overlying the outer defences, there are a number of structures, either taking the form of subrectangular structures with walls (and in one case an entrance) or simple scoops into the slope.
Visited by RCAHMS (JRS, IP, GG and AM) 2 August 2013.